
What Are the 10 Must-Have CMS Features for Higher Education?
Higher education institutions require a robust content management system to organize their digital presence and engage diverse audiences (including students, faculty, and other organizations). In this article, we present a comprehensive look at the top ten must-have CMS features that will enable universities to easily manage their websites while providing an efficient, secure, and user-friendly digital experience for all audiences.
1. User-friendly editing interface
Faculty and staff are experts in their fields but not necessarily in web development or programming. That’s why they need an intuitive editing interface that simplifies creating and managing content. It enables these non-technical users to contribute their expertise and insight directly to the website without relying on the IT department.
The ability to update course information, research findings, event details, and news articles in real time is essential. An easy-to-use CMS interface facilitates timely updates and adjustments, ensuring that the institution's website remains current and accurate. It reflects well on the institution's reputation and supports its operational and educational goals by providing up-to-date information.
CKEditor 5 in Drupal 10, the example of an easy-to-use editor
CMSs typically have built-in WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) editors - for example, Drupal 10 has CKEditor 5. They can include drag-and-drop functionality, user-friendly content creation tools, and pre-designed templates, making it easier to maintain a consistent look and feel across the website. These options can significantly reduce the time and effort required to publish new content.
2. Workflows for editorial review and publishing control
Effective content management requires a system of checks and feedback. A CMS solution with content workflow capabilities for editorial review and publishing controls ensures that all texts align with institutional standards before going live. It helps maintain content quality and brand consistency.
In the context of higher education, where the information presented can influence the decisions of prospective students, funders, and research partners, the stakes are incredibly high. These content workflows allow designated reviewers to review texts for accuracy, relevance, and adherence to the institution's messaging and ethical guidelines. It also prevents the spreading of outdated or incorrect information.
What does this workflow look like? For instance, a faculty member can draft an article about a new research breakthrough. Then, the research team can review it for scientific accuracy and submit it to the grants office to check for compliance with funding requirements. Finally, the communications department approves the article for publication.
3. Built-in SEO tools as a CMS feature
SEO tools are essential for ensuring content visibility and high search engine rankings. They help institutions stay competitive in search engine results and attract more prospective students.
What are some examples of built-in SEO features that you'll find most often in CMS systems?
- Customizable URL structures: thanks to this option, editors can create intuitive and keyword-rich web addresses. It increases the web page's SEO ranking, as search engines favor URLs that clearly describe the content.
- Redirect management: as websites evolve, pages move or get deleted, which can lead to broken links. Built-in redirect management allows for redirecting old URLs to new ones, preserving link equity, and ensuring visitors find what they want.
- Image optimization tools: websites for higher education are often media-rich. Built-in tools for image optimization, including file size reduction and alt text addition, ensure that images enhance SEO while also improving page load speeds.
- Meta-tagging capabilities: meta tags provide search engines and users with information about a web page's content. Customizing meta titles and descriptions enables institutions to optimize each page for relevant keywords.
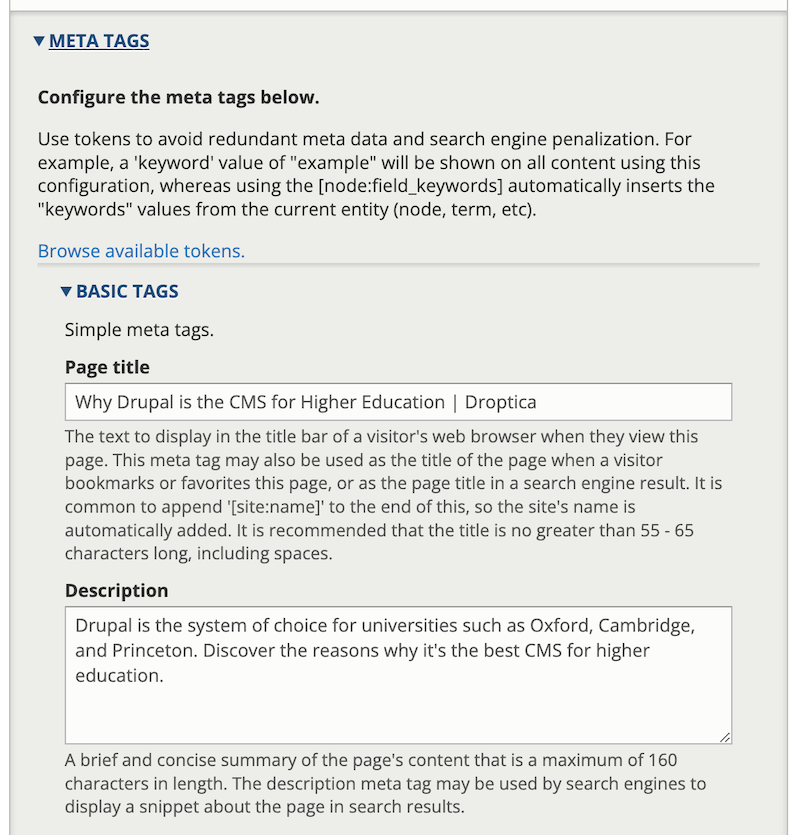
An example of a built-in section in the editor for completing meta tags
4. Multi-site functionality
Another important CMS feature is the multi-site functionality. It’s particularly beneficial for large universities that operate across various campuses or offer a wide range of programs. This feature allows each department, faculty, or program to have a distinct website under the institution's main digital umbrella while enabling central oversight and control.
From a practical standpoint, this means that while the marketing department can ensure consistent branding across all platforms, individual departments can tailor their content to their specific audience's needs. This balance between autonomy and coherence is crucial for presenting a unified brand image to the public, improving navigation between sites, and enhancing the user experience for students, faculty, and prospective applicants.
Furthermore, multi-site functionality streamlines the technical maintenance of these websites. Central IT departments can simultaneously apply updates, security patches, and new features across all pages. It reduces the workload and ensures that each site is secure and grows with the technology used.
5. Advanced security CMS features
In higher education, where institutions handle vast amounts of confidential data (including student records, financial information, and research data), the importance of implementing advanced security measures cannot be overstated.
Here are some examples of critical components of a secure CMS:
- SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certification: assures that data transmitted between the user's browser and the CMS is encrypted, making it virtually impossible for hackers to intercept and decipher.
- Regular security updates: a chosen content management system must stay ahead through continuous updates and patches. They close vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit, ensuring the institution's digital infrastructure remains impervious to new hacking techniques and malware.
- Strong authentication methods: they’re essential for verifying the identity of users and protecting against unauthorized access. For example, multi-factor authentication (MFA) requires users to provide two or more verification factors to access the CMS, significantly reducing the risk of data breaches.
6. Permission and user role administration
A sophisticated CMS allows for creating customizable user roles and permissions (on the access control lists) that match the unique structure and needs of the institution. For example, roles can be tailored for content creators, editors, departmental administrators, and IT staff, each with access levels appropriate to their responsibilities. This customization ensures that users have the tools and access they require to perform their roles effectively without exposing the system to unnecessary risk.
With clearly defined roles and permissions, every action taken within the CMS can be tracked and attributed to individual users. This creates an audit trail that can be invaluable for troubleshooting issues, conducting security audits, or resolving disputes over content changes. The transparency and accountability provided by detailed user administration enhance security within the institution.
By limiting access to sensitive features and content, institutions can also significantly reduce the risk of accidental or malicious data breaches. For instance, only a few administrators might be able to access student information or financial data. At the same time, a broader group of users can post news updates or event information.
7. Accessibility CMS features
A CMS with robust accessibility capabilities is equipped with tools and features designed to make web content available to people with a wide range of disabilities. This includes visual, auditory, physical, speech, cognitive, and neurological disabilities. The goal is to ensure all users can perceive, understand, navigate, interact with the web, and contribute content.
Here are examples of accessibility features in CMS systems:
- Alternative text for images: to ensure that users who cannot see images can still understand their content, the CMS should make adding alternative text descriptions to all images easy. This text is a substitute, conveying the same message or purpose as the visual.
- Keyboard navigation support: the CMS must support keyboard navigation for users who cannot use a mouse. This means users should be able to access all content and navigate the site using keyboard commands alone.
- Contrast and color options: the CMS should allow for color schemes and contrast adjustments to accommodate users with visual impairments, including those with difficulty perceiving specific colors.
- Compliance with WCAG and other standards: the CMS should also facilitate compliance with the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) and other relevant standards, ensuring that the institution's digital content meets the latest accessibility criteria.
8. Multi-language support
By offering content in multiple languages, institutions can significantly widen their reach, making their websites more welcoming and easier to navigate for international visitors. This helps show respect for cultural differences and linguistic identity, fostering a stronger bond between the institution and its audiences from different countries.
Multi-language support in CMS systems is also instrumental in global marketing and recruitment efforts. It allows institutions to tailor their messaging to resonate with diverse audiences and improve their visibility in international search engine results.
Using multi-language capabilities in a CMS involves careful planning and strategy, including selecting relevant languages based on the institution's users and strategic goals. It also requires maintaining high content quality and consistency across all languages. This ensures every user receives the same level of information and engagement from the authors, regardless of language preference.
9. Handy media management
Efficient media management tools are essential for handling the vast amounts of images, videos, and documents on higher education websites. A CMS should offer easy uploading, organization, and embedding capabilities to streamline media handling.
An example of media management in Drupal, a good CMS for higher education
These systems typically include features such as automatic image and video resizing and optimization. This ensures that media content doesn’t negatively impact page load times, a critical factor for user experience and SEO rankings.
Robust media management tools should support advanced tagging and categorization, enabling users to easily find and reuse media across the institution’s digital assets. This increases the efficiency of content creation and ensures consistency and accuracy of media representation across different channels and sites.
10. Social media and third-party system integrations
Social media integration within a CMS allows institutions to effortlessly connect their content with popular social platforms like Facebook, X, or LinkedIn. It enables the seamless sharing of news, events, and educational resources. This direct pathway amplifies the institution's visibility and cultivates a more engaged community by encouraging interaction among students and faculty.
On the other hand, integrating third-party systems into the CMS architecture significantly elevates an institution's operational efficiency and service delivery. By creating a seamless flow of information between the CMS and systems such as student information systems (SIS), email marketing tools, and customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, institutions can ensure a unified approach to student engagement, from recruitment to alumni communication.
This integrated process supports the strategic use of analytics, allowing institutions to gain a holistic view of engagement and effectiveness across all digital channels. By understanding how content performs, both on the university website and on social media, and how users interact with various institutional systems, decision-makers can refine strategies to meet better the institution's goals and the needs of its community.
CMS features for higher education - summary
Higher education institutions need a solid CMS to manage their online presence effectively. They require features that make websites easy to update, secure, and accessible to a global audience. Drupal offers all these must-have features, such as simple content editing, robust security, seamless social media integration, and support for multiple languages. According to our report on CMS usage at universities in Poland, many institutions have chosen this technology.
We understand how important it is for academic websites to utilize these features fully. That’s why our team specializes in Drupal services for higher education. We can help your institution build a website that attracts a diverse audience and is also ready to grow with you.











