
Website Security: Implement Best Security Practices in 30 Seconds
Protecting your website, web application, or CMS system from cyber attacks is critical to maintaining trust and functionality. Do you know how to secure it effectively? Follow our checklist of essential website security best practices in this blog post, and if you're using Drupal, you can apply them all in just 30 seconds with our recipe.
In this article:
- The growing importance of website security – key stats and reasons
- Essential website security practices for every website
- Website-specific security settings
- Why is Drupal a secure CMS?
The growing importance of website security – key stats and reasons
As cybercrime continues to escalate, the stakes for website security have never been higher. The global cost of cybercrime is projected to soar from $9.22 trillion in 2024 to $13.82 trillion by 2028 (source: Statista). This alarming growth highlights the increasing sophistication of targeted attacks, especially as businesses and individuals rely more on online platforms.
Websites and web apps are prime targets for these cyber criminals, making proactive security measures essential. With the right steps, you can protect your site from the most common security threats, avoid costly breaches, and maintain the trust of your users.
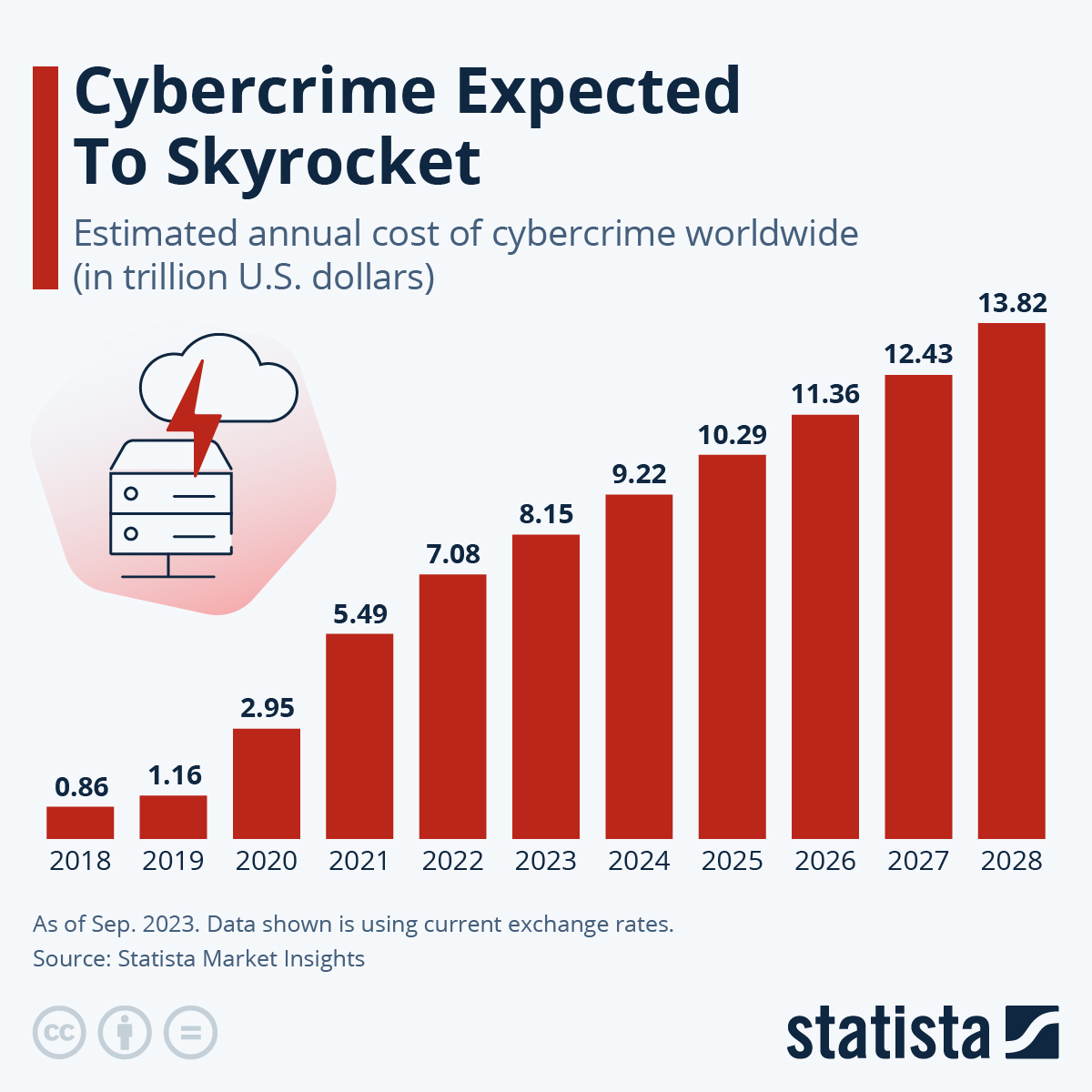
Why is website security important?
Given the alarming rise in cybercrime, website security is no longer optional but a fundamental necessity. Here are some key reasons why every online business must prioritize protection:
- Data leakage - if a website is not secured correctly, there is a risk of valuable data leakage (e.g., sensitive information). Both those of the organization and its customers are exposed. This can lead to significant financial losses and, even worse, a decline in user trust.
- Website interruptions and impact on SEO - cyber-attacks can disrupt website availability, leading to lost potential customers and decreased satisfaction among existing legitimate users. Website security also translates into its positioning in search results. Search engines such as Google penalize web pages that have accessibility problems caused, for example, by Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. As a result, they lower their ranking and, thus, spots where they appear to potential customers. For example, websites without an SSL certificate are flagged as ‘Not Secure’ by Google, which discourages website visitors and negatively affects rankings.
- Damage to brand image - website security also directly impacts a company's image. Security incidents can damage a business's reputation and can be time-consuming and costly to repair. For example, in 2017, credit reporting giant Equifax suffered a massive data breach, exposing the sensitive information of 147 million people (source: ftc.gov). The incident not only led to at least a $575 million settlement but also severely eroded consumer trust, causing long-term damage to the company’s reputation. This case highlights how a single security lapse can have lasting consequences for a brand.
Essential website security practices for every website
What is website security? It's an ongoing process that requires regular attention and frequent intervention. There are many effective strategies you can employ to secure a website. Here are some basic steps to help you keep your web page protected at the highest level.
SSL and HTTPS
A secure website connection relies on SSL certificates (also known as TLS—Transport Layer Security) and HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure). SSL encrypts the data exchanged between a user's browser and the server, preventing the unauthorized interception of sensitive information such as passwords, payment details, and personal data.
Modern web browsers flag sites without an active SSL certificate as “Not Secure,” which can discourage website visitors and negatively impact user trust. Additionally, Google prioritizes HTTPS-enabled sites in search rankings, making SSL essential for security and SEO.
Setting up SSL encryption is straightforward. Many hosting providers offer one-click SSL installation, and free services like Let’s Encrypt make it easy to implement HTTPS at no cost. Ensuring your website has an up-to-date SSL certificate is a fundamental step in protecting your users and maintaining credibility online.
Software and plugin updates
Outdated software is one of the most common entry points for cyberattacks. Hackers actively scan websites for known vulnerabilities in content management solutions, plugins, and third-party integrations, exploiting them to gain unauthorized access, inject malicious code, or steal sensitive data.
To prevent such risks, always keep your CMS, themes, and plugins up to date. Software vendors frequently release security patches that fix vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them.
To stay protected:
- Enable automatic updates whenever possible to ensure security patches are applied as soon as they’re released.
- Remove unused plugins and themes, as they can become security risks if left outdated.
- Regularly check for security advisories related to your CMS and extensions. Drupal, for instance, has a dedicated Security Advisory page that alerts users to potential security threats.
By maintaining updated software and proactively addressing vulnerabilities, you significantly reduce the risk of cyberattacks and ensure the long-term security of your website.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of website and CMS security by requiring at least two verification factors before granting access to an account. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized logins, even if an attacker has obtained the correct password (e.g., through a data breach or password guesses).
The most common form of MFA is Two-Factor Authentication (2FA), which typically involves:
✔ A temporary one-time code (TOTP) generated by an authenticator app (such as Google Authenticator or Microsoft Authenticator) that changes every 30–60 seconds.
Screen from the Google Authenticator application, source: play.google.com
✔ A physical security key, such as YubiKey or Titan Security Key, which must be physically plugged into a device or connected via NFC.
✔ Biometric authentication, like fingerprint scanning or facial recognition, used in some advanced authentication setups.
Why is MFA essential? Even if attackers gain access to your CMS or hosting account password, they cannot log in without the second factor. Whenever possible, use an authenticator app or a security key for stronger protection.
Regular backups
Backups are your safety net in case of security breaches, technical failures, or accidental data loss. Having recent, automated system backups allows you to quickly restore your site and minimize downtime, preventing significant disruptions to your business.
How to ensure maximum web security?
Secure your website or web application with some simple backup practices.
✔ Generate backups for both the database and website files. This ensures you can recover all critical data in case of an incident.
✔ Store backups in multiple locations, such as external storage devices and cloud services like Google Drive or Amazon S3, to prevent loss due to hardware failure or cyberattacks.
✔ Use a backup solution with version history, allowing you to restore an earlier, uncompromised version if needed.
✔ Regularly test your backups to verify they aren't corrupted and can be successfully restored—otherwise, you may discover too late that your safety net doesn’t work.
In the unfortunate event of a hacking attack or even a simple system crash, a reliable backup allows you to bypass the lengthy and costly process of repairing the damage. A well-structured backup strategy ensures that, no matter what happens, you can quickly recover your website and keep your data secure.
Web Application Firewalls (WAF) and DDoS Protection
A Web Application Firewall (WAF) helps protect websites from threats like SQL injection attacks, cross-site scripting (XSS), and malicious bot traffic by filtering and blocking harmful requests before they reach your web server.
While WAFs mitigate risks such as application-layer Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, they aren't enough to stop large-scale network-layer DDoS attacks. To fully protect your website, combine WAF with dedicated DDoS protection services like Cloudflare or AWS Shield, which filter out malicious traffic before it overwhelms your web server.
If using Cloudflare or similar services, ensure:
✔ All traffic is routed through the WAF/CDN, preventing direct server access.
✔ Firewall rules are regularly updated to block emerging website security threats.
✔ DDoS protection settings are configured properly to avoid downtime.
Additionally, Cloudflare and similar platforms can serve cached versions of your site, keeping it accessible even if the web server is temporarily offline. Implementing properly configured tools significantly enhances website security and reliability.
Regular security audits
Regular security audits, preferably conducted by a third-party cybersecurity company, will help protect your website to the highest standards. During such an inspection, experts can detect critical vulnerabilities (e.g., malicious code injections, outdated software, or misconfigurations) before they become real threats.
These audits provide a full security overview, helping you identify and fix weak points efficiently. With professional support, you not only get expert analysis but also assistance in resolving security issues and implementing long-term protection strategies.
Self-assessment - how can you tell if a website is secure?
While professional audits are the most reliable way to secure your site, as a website owner, you can take initial steps on your own to assess basic security aspects:
✔ Check SSL certificate validity – a valid SSL certificate ensures a secure connection between the browser and the web server. Look for the padlock symbol in the browser’s address bar. A missing or expired SSL certificate can compromise security and user trust.
Source: droptica.com
✔ Scan for malware – regularly check your website for malware using security tools or antivirus software to detect vulnerabilities before hackers exploit them.
✔ Ensure software is up to date – running an outdated CMS, plugins, or themes introduces serious security risks. CMS systems (such as Drupal or WordPress) usually allow you to verify updates directly from the administration panel.
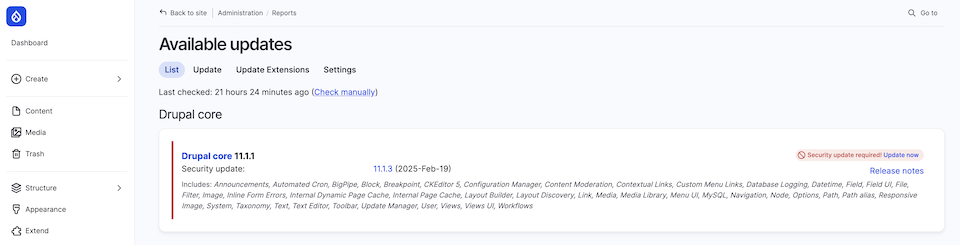
Source: droptica.pl/go/democms
Proactive security measures
Beyond self-checks, penetration testing and security reviews can uncover hidden vulnerabilities:
✔ Use OWASP ZAP for penetration testing – this open-source tool helps detect security weaknesses before attackers exploit them.
✔ Check HTTP Security Headers – tools like Security Headers evaluate whether your site is protected against clickjacking, XSS, and other attacks.
✔ Leverage CMS security reports – platforms like Drupal provide built-in security reports, making it easier to track and mitigate potential risks.
Although these self-assessments help identify common vulnerabilities, a comprehensive security audit from cybersecurity professionals is essential to detect hidden risks and implement tailored security solutions.
Website-specific security settings
Implementing website-specific security settings is essential for protecting user-sensitive data, preventing unauthorized access, and mitigating cyber threats. While general security practices like regular backups and software updates are crucial, additional configuration settings at the website level provide an extra layer of defense against potential attacks.
Below are key security tools and measures that every website or web application should implement, along with quick, actionable steps to enhance protection.
Password policy best practices
Weak or reused passwords are among the most common causes of website security breaches. Many cyberattacks exploit weak credentials through brute force attacks or credential stuffing, where attackers use leaked username-password combinations from past data breaches to access other accounts.
How to enhance site security?
✔ Use long, complex, and unique passwords for each account, combining uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
✔ Avoid common words or patterns, such as "password123," or personal information like your name or birthdate.
✔ Enable a password manager (such as Bitwarden or Google Password Manager) to securely store and generate complicated passwords, reducing the risk of forgetting them.
Bitwarden - the example of a password manager
Instead of frequently changing passwords (which can lead to weaker choices), it's more effective to combine strong passwords with the Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) mentioned above. MFA adds an extra layer of security, making it significantly harder for attackers to gain access, even if they obtain your password.
Email notifications for account changes
Monitoring account-related changes is an effective way to detect suspicious activity early. Enabling email notifications for critical account modifications helps alert users, site owners, and administrators to potential unauthorized access attempts.
To improve site security:
✔ Enable email alerts for password changes so users are immediately notified if their login credentials are updated.
✔ Send notifications for email address modifications to prevent attackers from hijacking accounts.
✔ Monitor user role and permission changes to detect privilege escalations, ensuring that administrative access isn’t granted without proper authorization.
By implementing these notifications, website owners can quickly respond to unauthorized actions and prevent account takeovers.
Automated logout and session limits
Inactive sessions pose a security risk, especially when users access their accounts from shared or public devices. Automated logout and session limits help mitigate the risk of unauthorized access.
To protect user sessions:
✔ Set time-based automatic logout to terminate inactive sessions after a defined period (e.g., 15-30 minutes).
✔ Restrict the number of active sessions per user, preventing multiple simultaneous logins from different devices and reducing the risk of session hijacking.
✔ Implement session timeout warnings, allowing users to extend their session if they are still active.
These measures reduce the risk of unauthorized access in cases where a logged-in session remains open on an unattended device.
Login form security
The login page is one of the most targeted areas of a website by attackers attempting brute-force attacks or credential stuffing. Strengthening login security significantly decreases the risk of unauthorized access.
To improve login security:
✔ Use CAPTCHA to prevent automated brute-force login attempts.
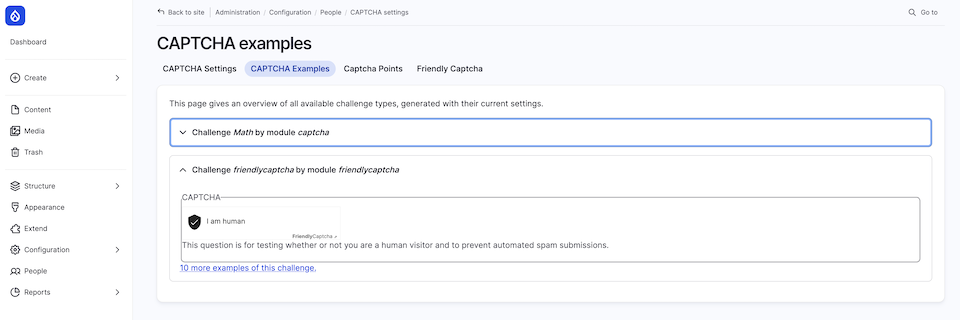
Source: droptica.pl/go/democms
✔ Implement the mentioned MFA to add an extra security layer, ensuring attackers can’t access an account with just a stolen password.
✔ Limit login attempts to block repeated failed logins and reduce the risk of password-guessing attacks.
These site security measures make it significantly harder for attackers to exploit login forms and gain access to user accounts.
HTTP headers security settings
HTTP headers play a crucial role in protecting a website against various web-based attacks, such as clickjacking, cross-site scripting (XSS), and content injection. By configuring secure headers, website owners can reinforce browser-level security and reduce attack vectors.
Recommended security headers:
- X-Frame-Options: prevents clickjacking attacks by restricting iframes from embedding your site.
- Strict-Transport-Security (HSTS): enforces HTTPS, ensuring all connections remain encrypted.
- Content Security Policy (CSP): mitigates XSS attacks by defining trusted content sources.
To simplify the implementation of security headers, use modules like Security Kit (for Drupal) or web server configurations that apply these settings automatically. Properly configured headers strengthen a website’s defense against client-side attacks and unauthorized content manipulation.
Why is Drupal a secure CMS?
Security is a top priority for any content management system, and Drupal stands out as one of the most secure CMS options available. Its dedicated security team, transparent update process, and substantial community support help to avoid security problems and make it an excellent choice for websites that require robust protection against cyber threats.
Why Drupal excels in security
Drupal provides website owners with the following:
- Regular security updates – this CMS has a weekly security release window every Wednesday, ensuring that vulnerabilities are patched quickly before they can be exploited.
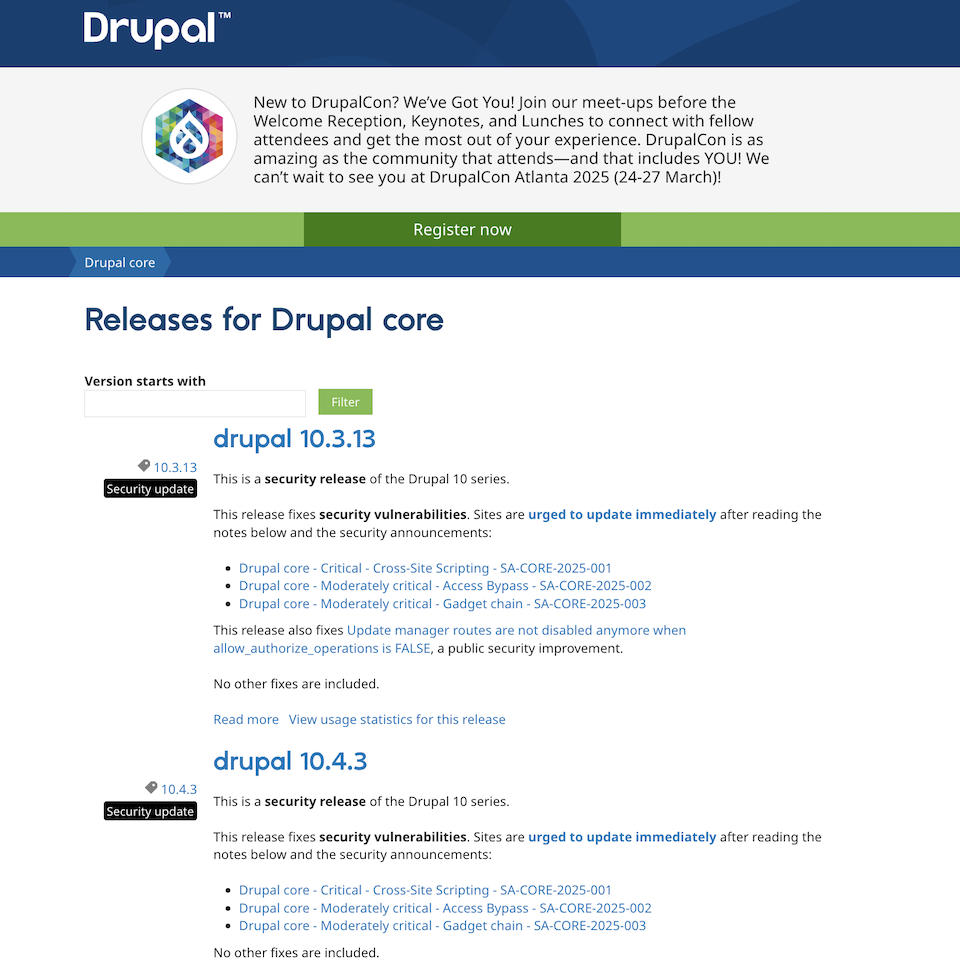
Source: Drupal.org
- Strict coding standards – the Drupal community follows rigorous security best practices, reducing the likelihood of vulnerabilities in core and contributed modules.
- Granular user permissions – Drupal’s built-in role-based access control (RBAC) allows precise control over user permissions, minimizing security risks from unauthorized access.
For a deeper comparison of Drupal’s security advantages over other CMS platforms, check out our full article: Why Drupal is more secure than other CMSs.
Implementing site security with Drupal modules
Drupal’s modular architecture makes it easy to extend and enhance security using contributed modules. Instead of implementing security features manually, site administrators can install and configure security modules that enforce best practices.
- Password Policy – enforces powerful password requirements (length, complexity, expiration rules).
- Captcha / reCAPTCHA – prevents automated bots from brute-forcing login forms.
- Security Kit Module – adds essential HTTP security headers (e.g., Content Security Policy, X-Frame-Options, HSTS) to protect against XSS and clickjacking attacks.
- Automated Logout – automatically logs out inactive users to prevent unauthorized access.
- Login Security – limits login attempts, blocks repeated failed logins, and improves authentication security.
By configuring these modules, Drupal users can quickly strengthen their website’s defenses without needing extensive security expertise.
How to implement all security in Drupal in 30 seconds
Setting up robust security in Drupal doesn’t have to be time-consuming. Instead of configuring security settings manually, Droptica’s DDR Security Recipe automates the process, ensuring that your site is secured in under 30 seconds.
What does the DDR Security Recipe do?
✔ Enforces strong passwords with Password Policy.
✔ Activates CAPTCHA to protect login and form submissions.
✔ Enables SecKit for essential HTTP security headers.
✔ Configures automatic logout for inactive users.
✔ Limits login attempts to prevent brute-force attacks.
How to apply it:
- Install the DDR Security Recipe according to the instructions on GitHub.
- Run the configuration process.
- Enjoy preconfigured security settings without manual adjustments.
Source: github.com/droptica/ddr_security
With this simple example of Drupal recipes, securing a Drupal site has never been easier.
Consider switching to Drupal for easy website security
If your current CMS lacks built-in security features or requires complex configurations to stay protected, it might be time to consider switching to Drupal.
Why?
- Security is built-in – no need for excessive third-party plugins or manual tweaks.
- Flexible security settings – granular control over user roles, authentication methods, and security policies.
- Easier compliance – Drupal makes it easier to meet GDPR, HIPAA, and other security regulations.
Whether you're managing an enterprise website, an e-commerce store, or a government platform, Drupal offers a secure, stable, and scalable foundation. If security is a priority, Drupal makes it easier to keep your site protected with minimal effort.
Website security measures and best practices - summary
Remember that website security is not just about technology but also about awareness, good management practices, and the use of security tools. Particularly important is the responsibility for the organization's and users' data and, as a result, concern for customer trust.
Taking care of security issues such as regularly updating software and plugins, using an SSL certificate and strong passwords, creating backups, using web application firewalls, and regular audits will definitely increase the security level of your web page.
Continuous monitoring and understanding of website security threats is key to maintaining the highest level of security. If you need help analyzing your website for protection, opt for the support and website security service of an experienced Drupal agency.
***
Updated article dated 28/09/2023












